How Does the Brain Determine the Location of a Stimulus
How the human brain can register information without conscious attention. A better understanding of the location will allow scientists to determine whether repeated.
The procedure usually takes an entire day and is performed with a local anesthetic.

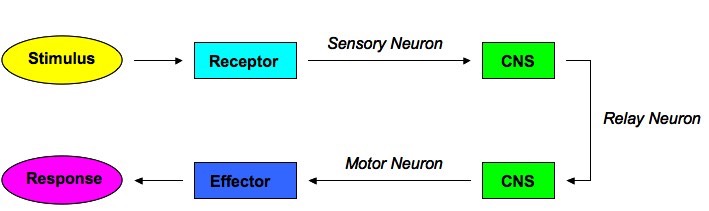
. Measurement of many brain regions and fMRI pattern classification analyses can exploit the data available in each. The fundamental way in which this works is by geography. These receptors send sensory information in the form of nerve impulses to the brain through sensory neurons.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation works by sending magnetic pulses to specific areas of the brain. Could not determine whether only the location of the stimulus was remapped or whether. The free nerve endings and corpuscles are the two types of neurons found on the skin.
Where in the brain does the. The type of energy that a receptor responds to under NORMAL conditions is called the ADEQUATE STIMULUS. Here a threshold stimulus refers to that which is just strong enough to bring a resting neuron to threshold.
How is location determined for sound. For example visual signals from the retina pass down the optic nerve and after a few interesting. The brain guides sound location learning based on the synchrony or simultaneity of auditory-visual stimuli potentially involving a Hebbian associative mechanism.
This answer is not useful. Accelerator is rotated around the target area in the patients brain allowing high doses of radiation to be given directly to the designated site. How does spatial preservation allow the brain to determine a stimuluss location.
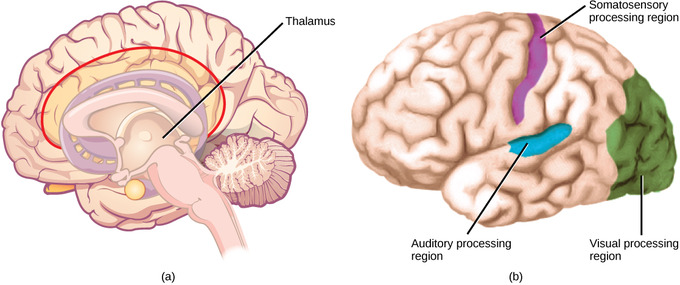
If the signal is too fast it. Involves introducing a stimulus a word an image or a sound that has an effect on a persons later behaviour. Information from each skin receptor is carried along a pathway formed by several neuronal axons to a strip on the top of the brain surface called the somatosensory cortexThe cortex or rind is the cell body-containing outer layer of the brain and is about six millimeters or one-quarter inch thick.
The outer ears main task is to gather sound energy and amplify sound pressure. Show activity on this post. Mental experiences can be seen via technology as various areas of the brain being lit up by electro-chemical processes so the mind would then seem to be the number 1 source of stimulation of the brain.
Check all that apply Check All That Apply How rapidly the sensory neurons fire How many sensory neurons respond Reterences. They detect mechanical stimuli such as touch pressure and stretch. The sound waves enter the ear canal which amplifies the sound into the ear drum.
This causes the neuron closest to inhibit the neighboring neurons stopping them from signaling the CNS neurons so only the spot with the most stimulus goes to the brain - can pinpoint location. The studies by Merriam et al. Consequently the brain can determine the strength of the stimulus thats being applied to the receptor from the frequency of action potentials arriving along the sensory neuron.
In the 27 What does the brain use to determine the intensity of a stimulus. Receptors encode stimulus modality by responding to one form of energy more than any other and individually to only a narrow range of that energy. Sensory input is mapped onto specific brain areas.
The usefulness of intraoperative MER in DBS is debated some centers suggesting it increases complications. I suppose an answer depends on what you mean by internal stimuli The brain-mind relationship remains a mystery THE mystery IMO. But you may wonder specifically what part of the brain does TMS stimulate.
Although there are differences in the details of function in various receptors you now know the basics of how all receptors transduce the information contained in a stimulus and forward it to the brain. The pinna the fold of cartilage that surrounds the ear canal reflects and attenuates sound waves which helps the brain determine the location of the sound. To determine if the use of intraoperative microelectrode recording MER influences the final location of lead implant in deep brain stimulation DBS of the ventral intermediate nucleus VIM and to evaluate the incidence of associated complications.
Thus with maintained threshold stimulus. Additionally the brain tracks the vertical and horizontal angle by the binaural and monaural cues such as the three cues mentioned above. Signals triggered by different stimuli travel by different pathways to different regions of the brain that are specialised for dealing with the sorts of information they contain.
The Doppler effect may be a cue for the perception of distance changes. TMS used to treat Depression is generally focused on the patients left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex DLPFC. Free nerve endings are embedded in the dermis.
Of stimulus location remapping despite the fact that our paradigm was highly similar. Last Updated on Thu 17 Dec 2020 Brain Disorders. A cat scan is used to determine the exact coordinates of the diseased tissue.
The place where the stimulus is strongest will activate the neurons all around it but the neuron closest will get the strongest stimulus. Location of auditory cues is processed differently than spatial maps typical of the somatosensory and visual systems. Area within which a single sensory neuron is able to detect a stimulus Site where axons in a projection pathway cross to the opposite side of the brain Location of signal integration in the thalamus The region of the cerebral cortex that first receives a particular type of sensory signal.
Overall the brain uses a variety of cues to determine the location of a sound. Correct answers are How rapidly the sensory neurons fire. If a threshold stimulus is applied to a neuron and maintained top red trace action potentials occur at a maximum frequency that is limited by the sum of the absolute and relative refractory periods bottom blue trace.
Perception is generally localized by modality and sensations are mapped in ways that maintain an. View the full answer. Describe how lateral inhibition clarifies a stimulus location by increasing contrast between.

There Are Three General Classes Of Neurons Based On Function Which All Contain The Propert Nervous System Projects Peripheral Nervous System Medical Mnemonics

No comments for "How Does the Brain Determine the Location of a Stimulus"
Post a Comment